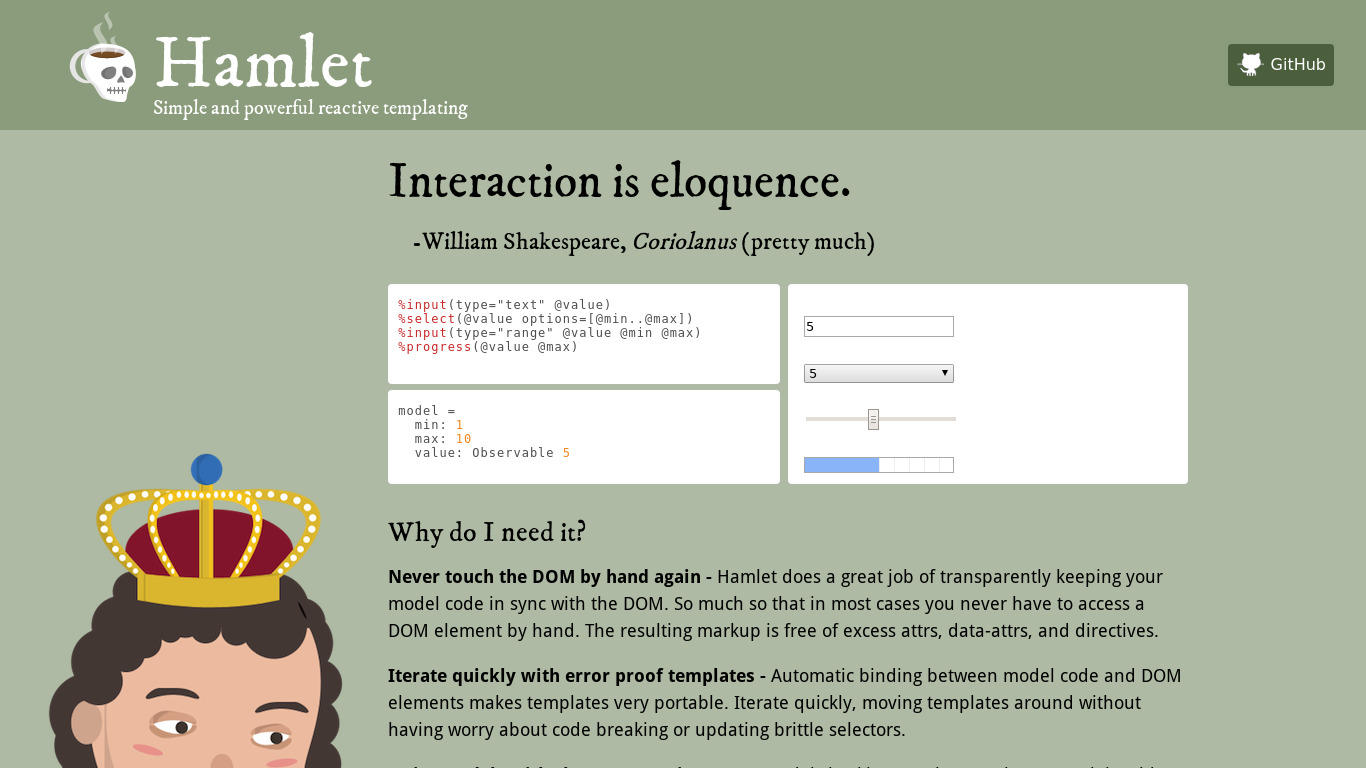
XSLT in-browser implementation VS Hamlet
Compare XSLT in-browser implementation VS Hamlet and see what are their differences

NinjaOne (Formerly NinjaRMM) provides remote monitoring and management software that combines powerful functionality with a fast, modern UI. Easily remediate IT issues, automate common tasks, and support end-users with powerful IT management tools.
featured